Capnography
Discover our directory of articles on Capnography in EMS, designed to equip professionals with the knowledge needed to effectively monitor and interpret end-tidal CO2 levels. This collection covers capnography in various scenarios, including respiratory emergencies, cardiac arrest, and airway management. Understanding capnography is essential for making informed decisions in critical situations. For more insights, explore our resources on Airway Management. Stay informed and improve your patient care with our expert guidance on capnography.
Learn how to effectively manage respiratory challenges during and after seizures
Learn how to detect pulmonary embolism through clinical symptoms and capnography, ensuring prompt and effective response
Assign someone to monitor the patient’s airway visually and with capnography using these five tips
A case study in opioid overdose complications, management strategies and provider safety
Learn how to assess, monitor and manage pediatric asthma emergencies, as well as underlying pathophysiologic changes
Teach EMS providers the benefits of waveform capnography in cases involving dyspnea and altered mental status, and before performing advanced airway management
Use high-fidelity patient simulation to teach ALS providers the danger and assessment of unplanned extubation
Titrating naloxone through an intranasal dose through a nebulizer and monitoring with capnography can reduce the risks of opioid withdrawal symptoms to the patient and EMS provider
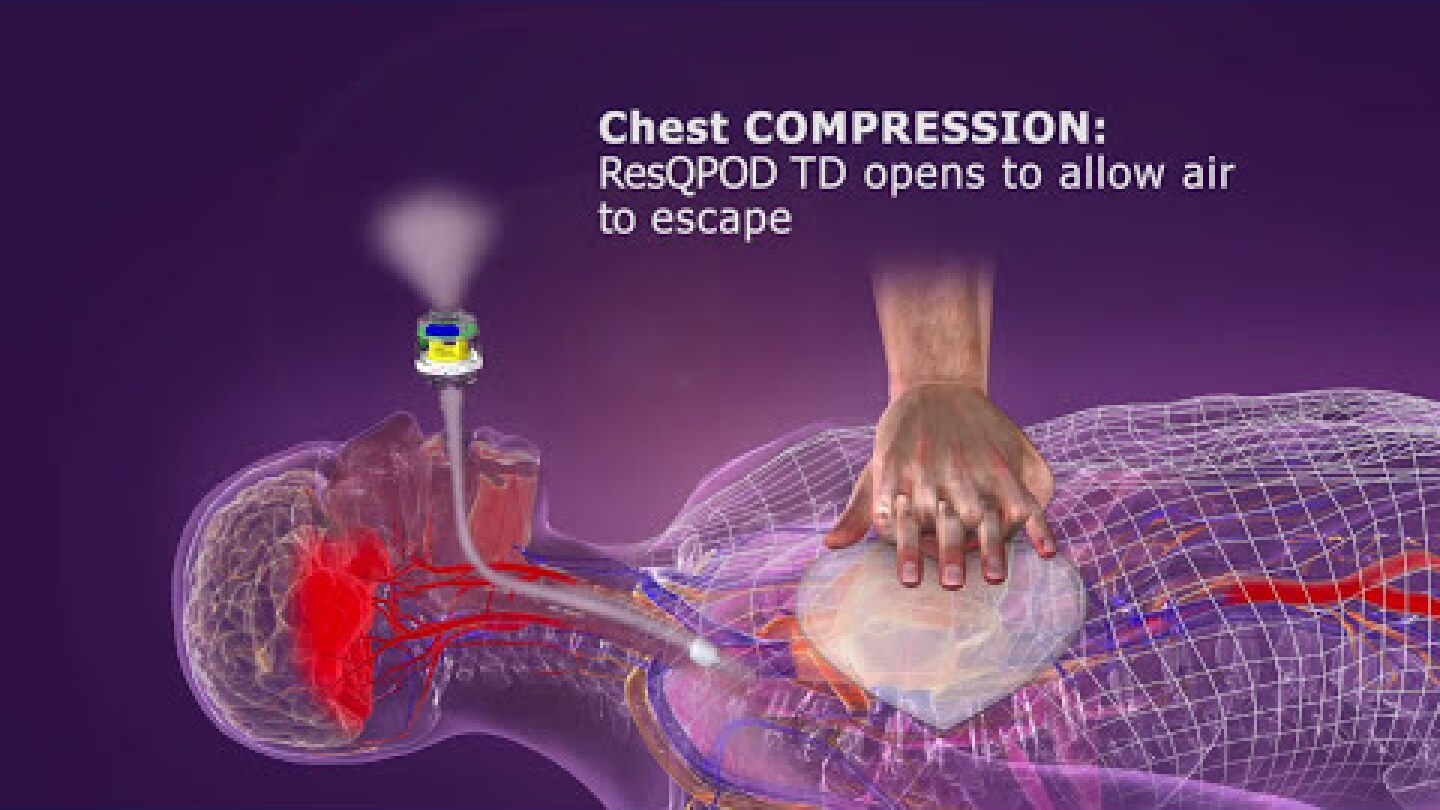
Dr. Dan Spaite shares how to avoid the potential pitfalls in positive-pressure ventilation, hyperventilation and over-ventilation
The flipped classroom is an inquiry-based learning strategy designed to improve student engagement, discovery and outcomes
A study of over 5,000 intubations demonstrates the value of continuous quality improvement
Take our 5-minute quiz to find out how your assessment skills measure up
When a patient’s life is in your hands, you need to know the risk factors, signs and symptoms of PE
Capnography experts will answer some of the most common questions first responders have
Through the EPIC treatment, EMS providers are taught to focus on the three H-bombs to prevent further damage to head injuries
A national database examining five metrics in evidence-based care gives EMS a framework to improve tactics, efficiency, outcomes and resource allocation
“From March 11 to 17, we are emphasizing that safety in the delivery of healthcare is the highest priority all the time,” CPS executive director Alex Christgen said
Understand the importance of realistic training on specific devices and using capnography to assess for effective ventilation through supraglottic airways
Video laryngoscopy may improve overall and first-pass success rates for ET intubation by paramedics
How much do you really know about supraglottic airway management uses, contraindications and techniques?
How well do you know the conditions associated with pH imbalances?
Test your knowledge on the challenges of assessing and treating children with capnography
The “set-up, size-up, scope, secure” mindset of the 1st and TEN approach to intubation may help improve first-pass success
A basic understanding of how acid-base imbalances can affect the patient’s presentation can help make sense of conflicting symptoms
Use simulation education to teach EMS providers to recognize and treat sepsis
An unconscious patient, with absent or ineffective breathing, may be in sudden cardiac arrest or have overdosed on an opioid; here’s how to assess and treat the patient
EMS educators can improve sepsis patient outcomes by ensuring EMTs and paramedics have knowledge appropriate and impactful training