Paramedics are the front line of emergency medical care. Whether responding to car accidents, heart attacks or natural disasters, these professionals are trained to make lifesaving decisions under pressure. If you’re interested in a rewarding career where you can make a real difference, understanding paramedic qualifications, training and how to become a paramedic is the first step.
Here’s a breakdown of how to become a paramedic, including qualifications, training, licensing, job opportunities and salary expectations.
What is a paramedic?
A paramedic is a highly trained health care professional who provides advanced prehospital medical care in emergencies. Paramedics are often part of emergency medical services (EMS) teams and respond to 911 calls involving serious injury or illness.
Unlike emergency medical technicians (EMTs), who are only trained to provide basic life support, paramedics undergo comprehensive training and can administer medications, start IV lines, interpret EKGs and perform advanced airway management. They work alongside firefighters, police officers and hospital staff to stabilize and transport patients. They may also work for private businesses and in other settings.
Why should I become a paramedic?
The biggest reason to become a paramedic is to help people in need. However, the qualifications to become a paramedic require dedication. Becoming a paramedic requires rigorous academic preparation and can subject you to long hours, high stress and distressing encounters and scenes.
To meet standard paramedic qualifications, you should:
- Be drawn to helping people in emergencies.
- Perform well under pressure.
- Have an interest in health care/medicine.
- Want to be active.
Benefits of becoming a paramedic include:
- Making a real difference in people’s lives.
- A job that’s dynamic and rarely boring.
- Strong job demand in many areas.
- It requires less training than becoming a doctor or nurse, so you can get started sooner.
Downsides of becoming a paramedic include:
- It can be stressful and emotionally demanding.
- Hours can be long and may include nights and weekends.
- It’s physically taxing and carries injury risk.
- You’ll see traumatic things, potentially impacting your mental health over time.
What qualifications are necessary to become a paramedic?
To become a paramedic requires education, certification and hands-on training. Typical steps may include:
1. Complete your high school diploma or GED
This is required to enroll in EMT or paramedic training programs.
2. Become an EMT (Emergency Medical Technician)
Start here before advancing to paramedic training. Becoming an EMT requires about 120–150 hours of training and can be done in a few months. This will cover areas like CPR, basic life support, trauma response and emergency protocols.
You’ll need to pass the National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians’ EMT exam before applying to a paramedic program.
3. Complete a paramedic program
As a certified EMT, you can apply to a paramedic program – this is the heart of paramedic training. These programs are typically 1,200–1,800 hours long and can take 1–2 years to complete, which is often done through a community college or technical school. The paramedic curriculum is more advanced than the EMT curriculum, involving cardiology, pharmacology, patient assessment and advanced airway management. Paramedic programs include clinical rotations in hospitals and ride-alongs with local EMS.
Paramedic training programs include advanced coursework in:
- Anatomy and physiology
- Advanced life support techniques
- Trauma management
- Pharmacology
- Cardiology
- Emergency childbirth
- Patient assessment
- Clinical and field internships
4. Get certified as a paramedic
After completing paramedic training, you can take the NREMT-Paramedic exam. States may also have their own exams or additional requirements to become a paramedic.
5. Get licensed as a paramedic
Each state has its own paramedic licensing process. They commonly involve background checks, proof of training and NREMT paramedic certification.
An associate’s degree in paramedicine can be helpful and is offered in some programs alongside paramedic certification.
Advanced certifications like ACLS (Advanced Cardiac Life Support), PALS (Pediatric Advanced Life Support) and PHTLS (Prehospital Trauma Life Support) can also improve your paramedic practice and job prospects.
How long does it take to become a paramedic?
A common question about how to become a paramedic concerns the duration of training. If you are starting your paramedic career journey without any medical training, it can take 2–3 years to earn your paramedic license, allowing for six months to earn your EMT certification and then an additional two years, give or take, to complete paramedic training:
- Step 1 — EMT certification: Around 6 months
- Step 2 — Paramedic training program: 12–18 months
- Step 3 — Licensing and exams: 1–3 months
Some accelerated programs may allow you to finish more quickly, while part-time programs may take longer.
Time commitment is a big factor. In addition to the requirements above, it may be valuable to spend time working as an EMT between gaining EMT certification and beginning paramedic training. Some paramedic programs prefer or require working experience.
The total estimated time required to become a paramedic can be as short as around two years, with no delay between EMT and paramedic school, or closer to 2½–3 years with EMT work included.
Where can I look for paramedic jobs?
Once you meet paramedic qualifications, jobs are in high demand across the U.S., especially in rural and underserved areas. You can find paramedic jobs with:
- Ambulance services
- Private EMS agencies
- Fire departments
- Hospitals and trauma centers
- Air medical transport services
- Private event and industrial safety teams
- State and local government agencies
Look for listings on job boards on industry-specific sites like EMS1, as well as traditional sites like Indeed and Glassdoor.
What is a paramedic’s salary?
Paramedics, due to their higher level of training and responsibility, typically earn a higher salary compared to EMTs. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the annual median wage as of May 2024 was $58,410 for paramedics and $41,340 for EMTs.
Overall employment of EMTs and paramedics from 2023 to 2033 is projected to grow by 6%, with more than 19,000 new openings anticipated each year.
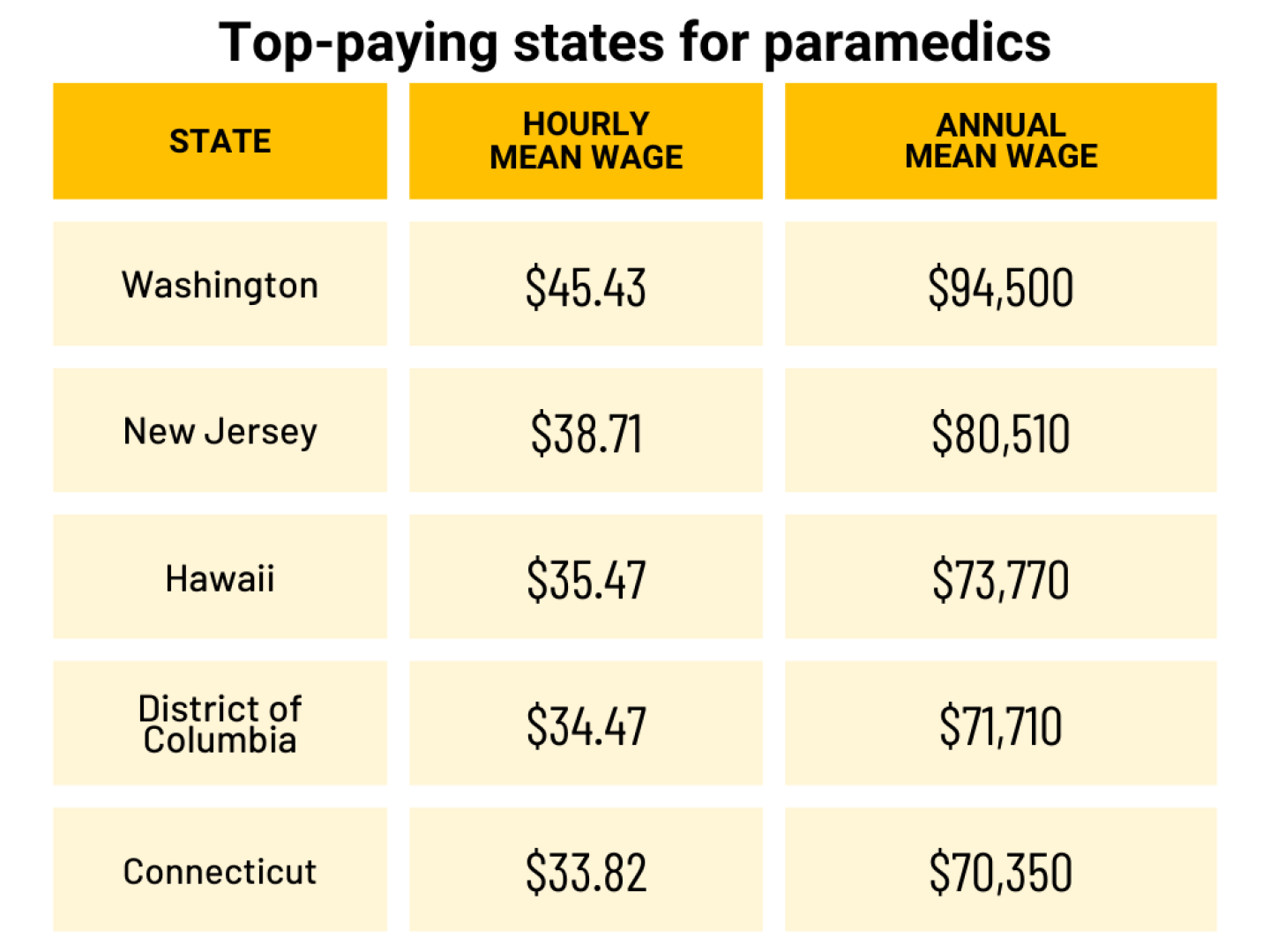
In what states do paramedics earn the most?
Paramedic salaries are highest in:
- Washington, averaging around $94,500 a year
- New Jersey, $80,510
- Hawaii, $73,770
- District of Columbia, $71,710
- Connecticut, $70,350
EMT salaries are highest in:
- Hawaii, averaging around $56,790 a year
- Maryland, $54,110
- Alaska, $53,080
- California, $52,100
- Massachusetts, $49,500
Higher salaries often correspond with higher cost of living, so evaluate both salary and living expenses when considering employment.
How are paramedics licensed?
A paramedic license is the legal authorization issued by a state’s EMS regulatory body that allows an individual to practice as a paramedic. After passing the NREMT exam, you must apply for licensure in the state where you plan to work.
Each state has its own licensing process, but most require:
- Proof of paramedic education
- Current CPR certification
- NREMT exam results
- Background check
- Continuing education for license renewal
What is the difference between a paramedic license and paramedic certification?
Understanding the difference between paramedic certification and paramedic licensure is key:
- Paramedic certification – This refers to passing the National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians’ (NREMT’s) paramedic exam. It validates your knowledge and skills at a national level.
- Paramedic license – This is granted by an individual state and gives you the legal right to work as a paramedic in that state.
Think of it this way: Certification proves your competence, while licensure grants you permission to practice.
What is required to continue working as a paramedic?
Once you’re working as a paramedic, you must continue to meet regular recertification and licensure maintenance requirements.
These may vary slightly from place to place but generally include:
Continuing education (CE) – The NREMT and most states require paramedics to complete continuing education every 2–3 years. This may involve refresher training (typically 30–60 hours) and skills verification through a hands-on assessment. Common topics include airway management, cardiology, trauma, pediatrics and medical emergencies.
Recertification – The NREMT requires nationally registered paramedics to renew every two years. This can be done through CE or by taking the paramedic certification exam. CE recertification requires 60 credits, with national, local/state and individual components. For the process for cognitive recertification, see the NREMT’s paramedic recertification page.
Additionally, nationally registered emergency medical responders (EMRs), emergency medical technicians (EMTs) and advanced emergency medical technicians (AEMTs) must also recertify every two years.
License renewal – Paramedic licenses are issued and renewed at the state level. States have their own paramedic licensing agencies and may have separate requirements beyond the NREMT’s.
Paramedic license renewal usually includes paying a fee, a background check or fingerprinting, and documentation of CE and any required certifications. Core certifications include Basic Life Support (BLS), Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) and Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS).
While the requirements to be a paramedic are arduous, the work itself can be extremely rewarding. Being a paramedic requires a dedication to the job that makes it more of an avocation than a vocation. It definitely isn’t the right choice for everybody, but for many, it’s the job of a lifetime.
This article, originally published in September 2016, has been updated with additional information.
EMS1 is using generative AI to create some content that is edited and fact-checked by our editors.